Fed Seen Elevating to 4% in 2022 And Signaling Larger for Longer
[ad_1]
(Bloomberg) — Join the New Financial system Day by day e-newsletter, comply with us @economics and subscribe to our podcast.
Most Learn from Bloomberg
Federal Reserve officers will sign a extra hawkish stance subsequent week, with rates of interest reaching 4% by December and staying excessive by 2023, economists surveyed by Bloomberg mentioned.
The Federal Open Market Committee will elevate charges by 75 foundation factors for a 3rd consecutive assembly when coverage makers announce their choice at 2 p.m. in Washington Wednesday, the survey discovered.
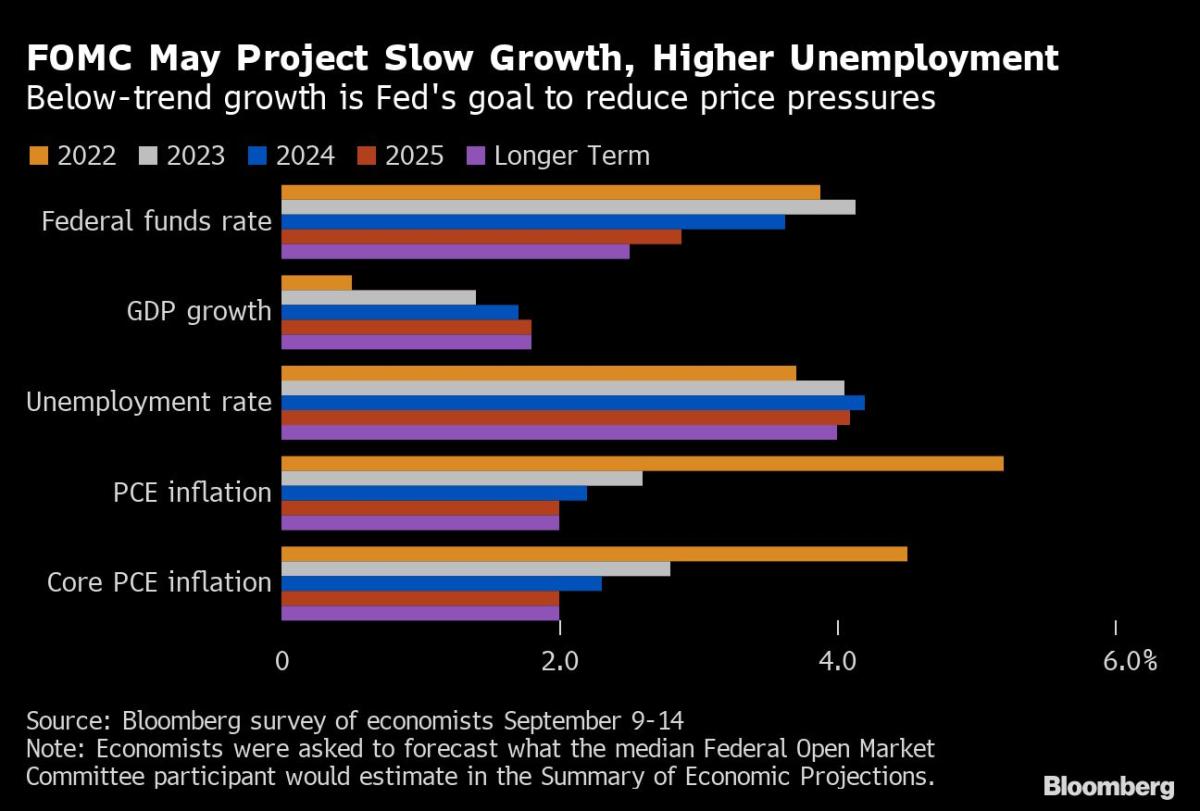
That might carry the goal vary for his or her coverage benchmark to three% to three.25%. Fed forecasts launched on the assembly are anticipated to indicate the higher sure of the vary at 4% by year-end and edging larger subsequent 12 months, earlier than cuts in 2024 take it again to three.6%.
Such a shift represents an enormous step up from Fed forecasts in June, reflecting a harder struggle in opposition to inflation after August core consumer-price progress got here in hotter than anticipated. The survey of 45 economists was performed Sept. 9-14.
Chair Jerome Powell has mentioned the Fed is strongly dedicated to getting inflation again to the central financial institution’s 2% goal, and received’t cease its struggle prematurely within the face of weaker financial information. The case for extra aggressive motion has been solidified by Tuesday’s client value index report, which confirmed measures of underlying inflation rising greater than anticipated.
“We count on the Fed to proceed mountain climbing till realized inflation prints come down, with the August CPI launch including substantial urgency to the Fed’s job,” mentioned Robert Dent, senior US economist at Nomura Securities Worldwide Inc. “The longer inflation stays elevated, the extra considerations of a wage value spiral and/or inflation expectations unanchoring rise.”
What Bloomberg Economics Says…
“The ‘dot plot’ will present the next terminal charge in 2023. We expect it would go as much as round 4.2%, in contrast with 3.8% within the June SEP. Additionally, the decline in 2024 in charges wouldn’t be as steep as within the June SEP. It’d present a lower to round 3.8-4% in 2024, in contrast with 3.4% in June SEP.”
— Anna Wong, chief US economist
Powell has been imprecise about how excessive rates of interest may go and in July mentioned the Fed would make coverage “assembly by assembly.” That makes the FOMC’s “dot plot” forecasts of the goal charge a main focus for buyers when the committee meets Sept. 20-21. Powell will maintain a press convention Wednesday, half-hour after the coverage choice is launched.
The speed path which economists count on the FOMC to put out subsequent week is much less aggressive than the one foreseen by markets. Buyers absolutely count on a 75 basis-point improve on Wednesday and see charges advancing an additional share level by 12 months finish to round 4.23%.
The economists’ personal forecasts largely match what they count on from the Fed’s Abstract of Financial Projections, with charges peaking at 4% in December, then declining in 2024.
Powell is making an attempt to steer the financial system towards a “softish” touchdown of slower financial progress, a still-robust labor market and weaker inflation. That will probably be mirrored in FOMC forecasts for progress of simply 0.5% in 2022 and 1.4% in 2023 — each large downgrades from June — with unemployment rising to 4.2% in 2024 from 3.7% reported in August, in response to the survey.
“Coverage stays targeted on inflation with little proof of being conscious of slowing financial/employment information or declining charges of inflation,” mentioned Hugh Johnson, chairman of Hugh Johnson Economics LLC.
Inflation stays the central subject driving Fed coverage. The FOMC is more likely to keep its forecasts for value pressures and should challenge inflation of 5.2% for 2022, 2.6% for 2023 and a couple of.2% for 2024. That might imply lacking the Fed’s long-run inflation goal of two% till 2025.
Powell has emphasised that the central financial institution will probably be nimble in its rate-hiking plans and the FOMC in its prior assertion supplied solely free steering that ongoing will increase could be applicable. Three quarters of the economists count on the committee to repeat the steering, whereas many of the relaxation say the FOMC may say it expects the tempo of hikes to gradual, echoing Powell’s current public statements.
Two thirds of economists additionally count on a unanimous choice this month, with the FOMC protecting a united entrance behind Powell’s struggle in opposition to inflation. Thus far this 12 months, St. Louis Fed President James Bullard has dissented as a hawk and Kansas Metropolis Fed President Esther George in a dovish course.
There’s much less certainty round plans to shrink the Fed’s stability sheet. The extent at which maturing securities are allowed to run out ramped up this month to an annual tempo of about $1.1 trillion. Economists challenge that can scale back the stability sheet to $8.4 trillion by 12 months finish, dropping to $6.6 trillion in December 2024, in response to the median estimate.
Virtually half of these surveyed say officers will resort to outright gross sales of mortgage-backed securities, in step with their said choice to solely maintain Treasuries within the longer run. Amongst these anticipating gross sales, there’s a variety of views on when promoting would start, with a slight majority seeing it begin by 2023’s second quarter.
Wall Road economists have continued to boost considerations in regards to the potential for recession because the Fed tightens financial coverage amid headwinds together with larger meals and power costs amid Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
“Larger-for-longer inflation, more-aggressive Fed financial coverage tightening, and damaging spillover results from a weakening international backdrop will mix to push the US financial system into a gentle recession within the first half of 2023, in our view,” mentioned Oxford Economics chief US economist Kathy Bostjancic.
Economists had been combined in regards to the outlook, with 49% seeing a recession as probably within the subsequent two years, 33% seeing a while with zero or damaging progress probably and the remaining searching for the Fed to realize a mushy touchdown of continuous progress and low inflation.
Most Learn from Bloomberg Businessweek
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.
Source link